Objective
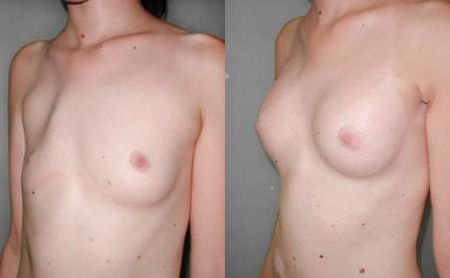
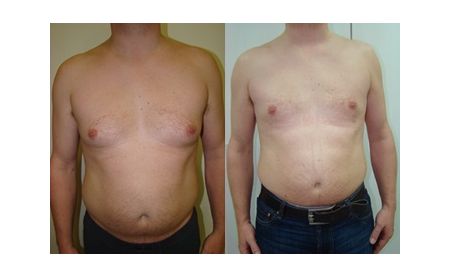
Reconstruction or compensation of the non-existing breast tissue after amputation or in the congenitally underdeveloped breast
Operative technique
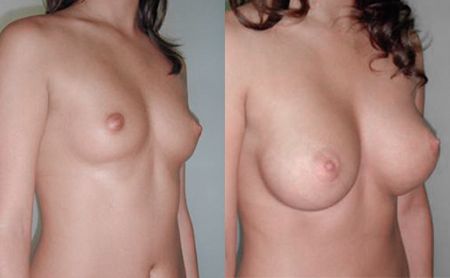
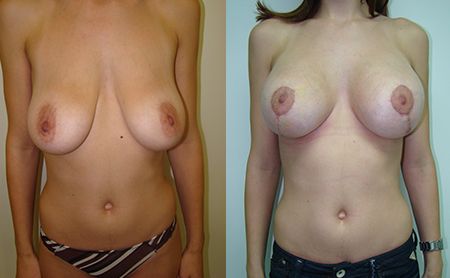
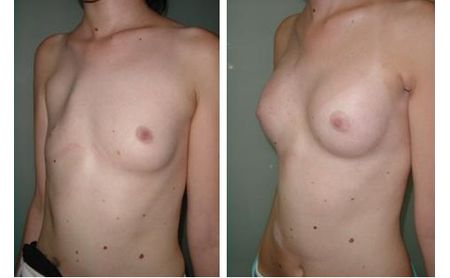
The amputated breast can be reconstructed in to ways, by means of silicone implant or with the own tissue. The application of implants is easier and simpler way, but as lack in skin is almost always present, first it has to be expanded with the expansion in the first act, by application of the so-called tissue expander, or Becker’s prosthesis – expander is first inserted, which remains permanently. In the next several weeks, the patient comes every 5 – 7 days when small amounts of physiological solution are inserted through a special spot on the skin, so that the implant gets gradually filled in up to the desired volume. The application of the own tissue from the abdomen or the back is also very much present in the breast reconstruction. However, the modern treatment of malignant diseases today also implies a primary reconstruction when the patient gets a compensation of the lost breast right after the amputation. Several months after the surgery, a possible additional correction may be performed, in terms of increasing the symmetry with the other breast (reduction and lifting of the other breast).
Duration of procedure and anaesthesia
Both operative techniques are performed in total anaesthesia, the first lasts around 1 – 1.5 hour, and the second much longer.
Recovery
Very short in inserting the prosthesis – expander, except that one should come several weeks for gradual volume increase. In reconstruction with the own tissue, or skin-muscle lobes, the recovery lasts much longer, as it is a large operative intervention.
Rare complications
Swelling, appearance of seroma which is drained longer, mild breast asymmetry, and in the reconstruction with the abdominal tissue, also a rare occurrence of abdominal hernia